-

Bangladesh targets $1b trade ties with Vietnam
-

VIETNAM COFFEE EXPORTS UNDER THE TOP 2 OF THE WORLD
-

Rice Exports by Country
-

Relations between Bangladesh and Vietnam
-

Bangladesh Economic Outlook 2019: A resilient economy in need of sound policy LIGHTCASTLE ANALYTICS WING
-

Bangladesh Economy Continues Robust Growth with Rising Exports and Remittances
-

Vietnam beats us in RMG for last 5 months in 2019
-
Bangladesh to seek more Vietnamese investment
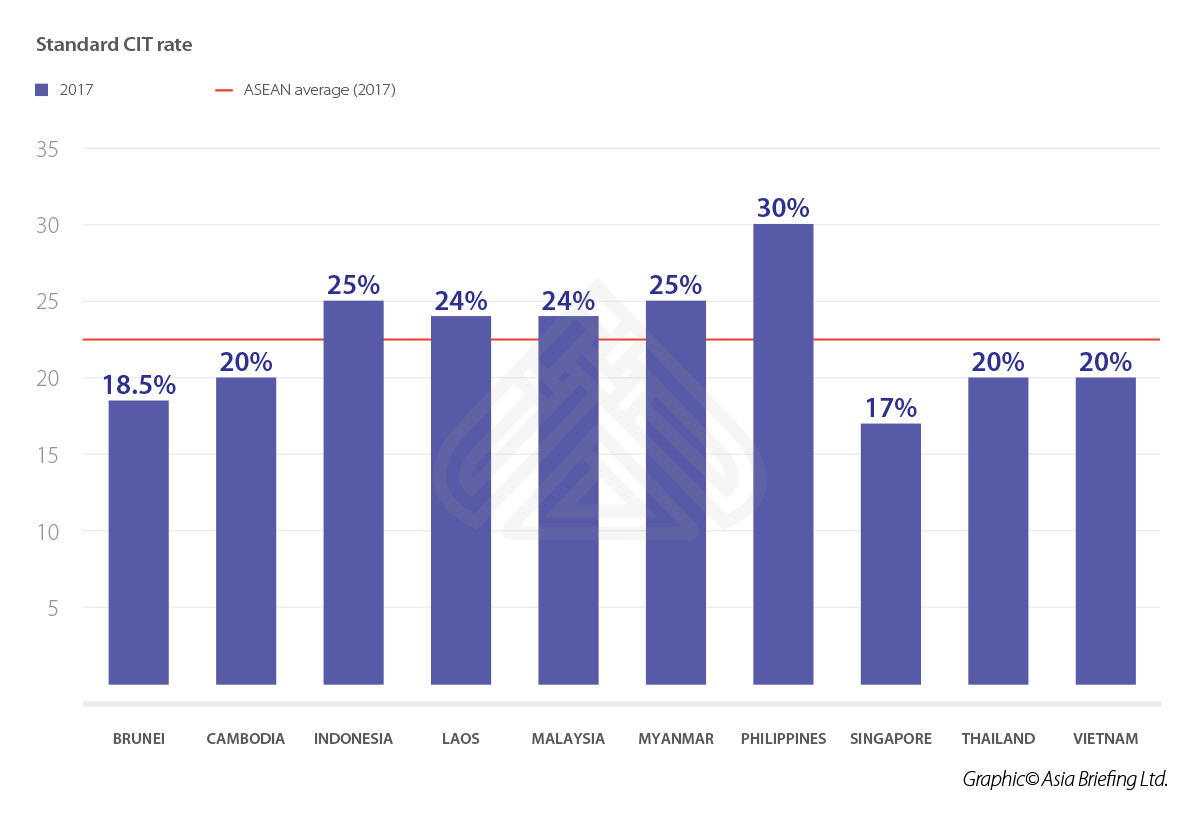
Vietnam’s major taxes
Many small and medium sized businesses are prioritizing investments in Vietnam and are acting on the business potential it holds. In this chapter, we examine the tax landscape so that new investors can better understand their in-country tax exposure before setting-up.
All taxes in Vietnam are imposed at the national level; there are no local, city, or provincialtaxes. Enterprises should pay tax in localities where they are headquartered or have duly registered branches. Most companies and foreign investors in Vietnam are subject to the following six major taxes:
• Business license tax;
• Corporate income tax;
• Value-added tax;
• Special consumption tax;
• Foreign contractor tax; and
• Customs duties.
Business license Tax (BLT)
BLT is an indirect tax imposed on entities conducting business activities in Vietnam, paid by enterprises annually for each calendar year that they do business in the country. All companies, organizations or individuals (including branches, shops, and factories) and foreign investors operating businesses in Vietnam are subject to BLT.
Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
All income arising inside Vietnam is subject to CIT, no matter whether a foreign enterprise has a Vietnam-based subsidiary, or whether that subsidiary is considered a Permanent Establishment (PE). CIT is a direct tax levied on the profits (gross revenue minus expenses) earned by companies or organizations.
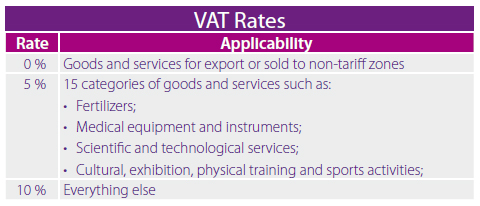
Value-added Tax (VAT)
VAT is imposed on the supply of goods and services at three different rates: 0, 5 and 10 percent, with the latter being the standard rate. All organizations and individuals producing and trading goods and services in Vietnam are liable to pay VAT, regardless of whether the organization has a Vietnam-based establishment.
Special Consumption Tax (SCT)
SCT is a form of excise tax that applies to the production or importation of 11 categories of products and six types of services which are considered to be luxurious or non-essential such as alcohol and tobacco products. Companies are liable for SCT both at the time of import and sale. However, to prevent an excessive tax burden, import SCT will be creditable against SCT incurred at the point of sale.
Customs duties
Most goods exported across the borders of Vietnam, or which pass between the domestic market and a non-tariff zone are subject to export or import duties. Exceptions to this include goods in transit, goods exported abroad from a non-tariff zone, goods which are imported from abroad into a non-tariff zone and only used within that non- tariff zone and goods passing from one non-tariff zone to another. Most goods and services being exported are exempt from tax.
Foreign Contractor Tax (FCT)
Foreign businesses and individuals without legal entity status are considered foreign contractors if they conduct business or earn income in the country under contract with local organizations including foreign owned companies. FCT, normally referred to as “withholding tax”, is not a separate tax type. It comprises of VAT and income tax (either CIT or PIT) imposed on payments of local organizations to foreign contractors. Such payments are considered income earned in Vietnam in which the Vietnamese parties are liable to declare and make payments on behalf of foreign contractors.
Payments subject to FCT include interest, royalties, service fees, goods supplied within Vietnam’s territories or associated with services rendered in Vietnam. The applicable tax rates vary depending on the payment method and the nature of the transactions. Certain distribution arrangements where foreign entities are directly or indirectly involved in the distribution of goods or provision of services in Vietnam are also subject to FCT.
FCT exemption is applicable in certain circumstances such as pure supply of goods, services
performed and consumed outside Vietnam and various other services performed wholly
outside Vietnam.
Individual Taxes
|
Individual Income Tax |
Tax rates from 5% to 35%. |
|
Less than VND 60,000,000 per year |
5% |
|
Between VND 60,000,000 and 120,000,000 per year |
10% |
|
Between VND 120,000,000 and 216,000,000 per year |
15% |
|
Between VND 216,000,000 and 384,000,000 per year |
20% |
|
Between VND 384,000,000 and 624,000,000 per year |
25% |
|
Between VND 624,000,000 and 960,000,000 per year |
30% |
|
From VND 960,000,000 per year |
35% |
|
Income from sources other than employment |
from 0.1% to 20% |
|
Non-resident employment income |
20% |
|
In response to the COVID-19 crisis, the deadline for payment of personal income tax has been extended to 31 December 2020. |
Allowable Deductions and Tax Credits
Social security, health insurance, and unemployment insurance are tax deductible, as well as contributions to local voluntary pension schemes and to mandatory overseas insurance schemes.
Charitable contributions are generally deductible. Severance allowances, redundancy compensation, and “non-accumulative” insurance premiums are not taxable.
All tax resident individuals are automatically entitled to a personal allowance of VND 9 million per month; plus an extra VND 3.6 million per month per dependent.
Special Expatriate Tax Regime
Individual residents are subject to Vietnamese personal income tax on their worldwide income, non-residents are subject to a 20% flat tax rate on the employment income received as a result of working in Vietnam. Business income of non-residents is subject to rates from 0.5% to 5%, depending on the type of business income.
An individual is deemed as resident for tax purposes if he/she: stays in Vietnam for 183 days or more in either the calendar year or the period of 12 consecutive months from the date of arrival; or has a permanent residence in Vietnam and is unable to prove tax residence in another country.
Copyrights Thiet Ke Website by ungdungviet.vn





